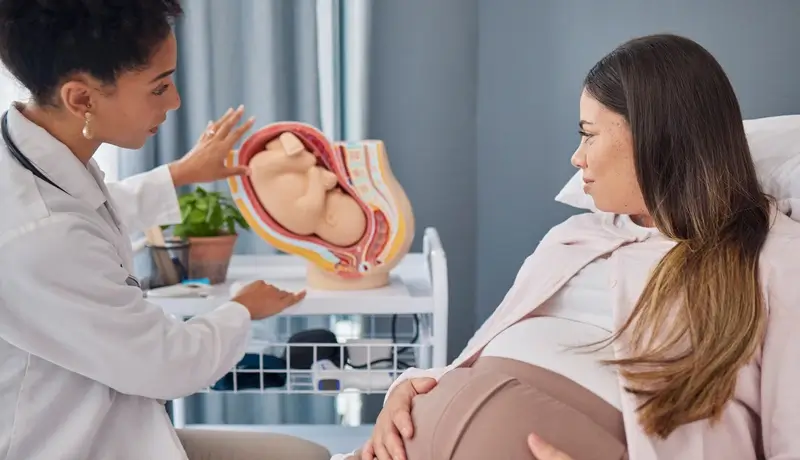
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
Pregnancy usually begins with a fertilized egg attaching to the uterine lining. In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants outside the main cavity of the uterus. Most ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tube, which connects the ovaries to the uterus, a condition called a tubal pregnancy. However, in rare cases, ectopic pregnancies can also occur in the ovary, abdominal cavity, or cervix (the lower part of the uterus connecting to the vagina).
Unfortunately, an ectopic pregnancy cannot proceed normally. The fertilized egg does not survive outside the uterus, and the growing tissue may cause life-threatening complications if left untreated.
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Initially, an ectopic pregnancy may not show any symptoms. Many women experience the usual signs of early pregnancy, including a missed period, breast tenderness, and nausea. A pregnancy test will likely show a positive result. However, since the fertilized egg isn’t in the uterus, the pregnancy cannot continue as usual.
Early Warning Signs
The first symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy often include light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain. As the fertilized egg grows in the incorrect location, more noticeable signs may appear. If blood leaks from the fallopian tube, you might feel:
- Shoulder pain
- Pelvic pain
- An urge to have a bowel movement
The symptoms you experience depend on where the blood collects and which nerves it affects.
Emergency Symptoms
If the fertilized egg continues to grow in the fallopian tube, it can cause the tube to rupture, which may lead to heavy internal bleeding. This situation is life-threatening. Symptoms of a ruptured tube include:
-
- Severe abdominal or pelvic pain accompanied by heavy vaginal bleeding
- Extreme lightheadedness or fainting
- Shoulder pain
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek emergency medical help if you experience symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, such as severe pain, heavy vaginal bleeding, dizziness, or fainting. Immediate treatment prevents complications and can save lives.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
The most common type of ectopic pregnancy, a tubal pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg gets stuck on its way to the uterus. This blockage often happens because of inflammation or an irregular shape in the fallopian tube. Hormonal imbalances and abnormal development of the fertilized egg may also play a role in ectopic pregnancies.
Risk Factors for Ectopic Pregnancy
Certain factors increase the risk of experiencing an ectopic pregnancy. These include:
- Previous ectopic pregnancy: Experiencing one ectopic pregnancy increases the chances of having another.
- Inflammation or infection: Sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea or chlamydia can cause inflammation in the fallopian tubes and nearby organs, raising the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Fertility treatments: Women who undergo in vitro fertilization (IVF) or similar treatments face a higher risk. Infertility itself may also contribute to an increased risk.
- Tubal surgery: Surgeries to repair or unblock the fallopian tubes increase the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy.
- Birth control method: Although pregnancy with an intrauterine device (IUD) is rare, it is more likely to be ectopic. Similarly, pregnancies occurring after tubal ligation have a higher risk.
- Smoking: Smoking just before pregnancy significantly increases the risk of an ectopic pregnancy, with heavier smoking raising the risk even more.

Complications of Ectopic Pregnancy
If left untreated, an ectopic pregnancy can cause a ruptured fallopian tube, leading to internal bleeding. This condition is life-threatening and requires immediate medical care.
Preventing Ectopic Pregnancy
Although it isn’t always possible to prevent an ectopic pregnancy, certain actions can reduce your risk:
- Practice safe sex: Reducing the number of sexual partners and using condoms helps prevent sexually transmitted infections, lowering the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Quit smoking: If you smoke, quitting before trying to conceive may reduce your risk of ectopic pregnancy.

Diagnosing Ectopic Pregnancy
To diagnose an ectopic pregnancy, your doctor conducts a pelvic exam and may order blood tests and ultrasounds.
Pregnancy Test
A blood test that measures human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) levels confirms pregnancy. HCG levels rise during a typical pregnancy, so doctors often repeat this test every few days to confirm or rule out an ectopic pregnancy, usually within five to six weeks of conception.
Ultrasound
A transvaginal ultrasound creates images of your reproductive organs, allowing your doctor to view the pregnancy location. During this test, a wand-like device in your vagina emits sound waves to produce images of the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. In some cases, an abdominal ultrasound may also check for internal bleeding.
Other Blood Tests
Doctors use a complete blood count (CBC) to check for anemia or other signs of blood loss. If an ectopic pregnancy is confirmed, they may also order tests to determine your blood type in case a transfusion is needed.
Treatment Options for Ectopic Pregnancy
Since a fertilized egg cannot develop outside the uterus, doctors must remove it to prevent complications. Treatment depends on the location and size of the ectopic tissue and the presence of internal bleeding.
Medication
For an early ectopic pregnancy without unstable bleeding, doctors often use a medication called methotrexate. This medication stops cell growth and dissolves existing cells. Doctors administer it by injection and use follow-up HCG tests to monitor its effectiveness. Additional doses may be necessary if HCG levels do not decrease as expected.
Laparoscopic Procedures
Salpingostomy and salpingectomy are two minimally invasive surgeries used to treat ectopic pregnancies. A small incision in the abdomen, near or in the navel, allows a thin tube with a camera (laparoscope) to access the fallopian tubes.
- Salpingostomy: The surgeon removes the ectopic pregnancy, leaving the fallopian tube to heal naturally.
- Salpingectomy: The surgeon removes both the ectopic pregnancy and the damaged tube.
The choice of procedure depends on the amount of bleeding, the extent of damage, and the condition of the other fallopian tube.
Emergency Surgery
If the ectopic pregnancy causes heavy bleeding, emergency surgery may be necessary. Surgeons can perform this procedure laparoscopically or through an abdominal incision (laparotomy). In some cases, they may save the fallopian tube, but often they must remove it to control bleeding and prevent further complications.
Coping and Support
Experiencing an ectopic pregnancy can be emotionally challenging. Give yourself time to grieve, and talk openly with your partner, family, or friends for support. Joining a support group or consulting a grief counselor may also help you cope with your feelings.
Many women go on to have healthy pregnancies after an ectopic pregnancy. If one fallopian tube is removed or damaged, the remaining tube can still function. For women with both tubes affected, in vitro fertilization (IVF) offers an option by allowing fertilized eggs to implant directly into the uterus.
Future Pregnancy and Monitoring
After an ectopic pregnancy, the risk of recurrence may increase. Regular check-ups and early blood tests are recommended for anyone trying to conceive again after an ectopic pregnancy. Early monitoring allows doctors to detect issues promptly and prevent complications.
Preparing for Your Appointment
If you experience light vaginal bleeding or slight abdominal pain, contact your doctor. Depending on your symptoms, they may recommend an office visit or immediate medical care. For severe symptoms, seek emergency help without delay.
Emergency Warning Signs
Recognize the signs that require urgent medical attention. Call 911 (or your local emergency number) or go to the hospital if you experience:
- Severe abdominal or pelvic pain with vaginal bleeding
- Extreme lightheadedness
- Fainting or dizziness
What You Can Do Before Your Appointment
To make the most of your appointment, consider preparing a list of questions and relevant health information. This can help you and your doctor discuss all necessary details efficiently. Here are some tips to get ready:
- Prepare Questions: Write down questions you might want to ask, such as treatment options, steps for future pregnancies, or follow-up care.
- Take Notes on Symptoms: Document any pain, bleeding, or other symptoms you have noticed, including when they started and how they feel.
- List Medications: Bring a list of any medications or supplements you are currently taking, as these may affect your treatment.
Conclusion
An ectopic pregnancy is a serious condition that requires immediate intervention to prevent complications. Recognizing the symptoms early, understanding the risk factors, and seeking prompt medical attention help ensure safety and well-being. Although experiencing an ectopic pregnancy can be distressing, many women go on to have successful pregnancies in the future with the right care and monitoring.
Remember to take care of yourself emotionally as well as physically during this time. Seeking support from family, friends, or support groups can be invaluable in helping you heal and move forward.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy in women with a history of infertility?
- Infertility or fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization, can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy, but the likelihood depends on various factors, such as the health of the fallopian tubes and medical history.
2. What are the effects of an ectopic pregnancy on future fertility?
- If an ectopic pregnancy is treated early, most women can have healthy pregnancies in the future. However, removal or damage to a fallopian tube may reduce a woman’s fertility.
3. What alternative treatment options exist if an ectopic pregnancy cannot be treated with medication or laparoscopy?
- In rare cases where medication or laparoscopic procedures are not possible or effective, open surgery may be required to remove the ectopic pregnancy and restore the woman’s health.
Request your Appointment by clicking on the picture below.



