Training for Maritime Medics

Maritime Medics require a broad range of medical skills to ensure the safety and well-being of crew members during voyages.
This comprehensive training program equips medics with the necessary knowledge and practical experience to perform essential medical procedures.
From understanding human anatomy to mastering advanced techniques such as venipuncture and tracheal intubation, participants will gain the expertise needed to handle very difficult medical emergencies at sea.
Anatomy
The teaching of anatomy to maritime medics is integrated with other clinical procedures. Bone anatomy is taught alongside a demonstration of a skeleton and X-rays of fractures.
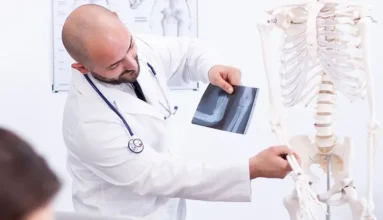
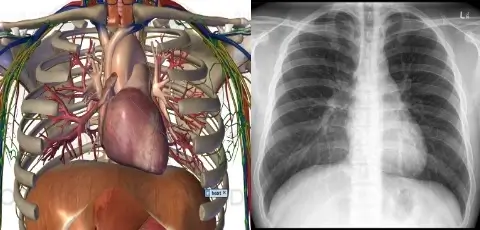
Neck anatomy is covered in parallel with Doppler ultrasound of the major vessels and practice in intubation. Chest anatomy is taught alongside X-rays showing pneumothorax, pneumonia, and pleuritis. The anatomy of the liver, pancreas, spleen, and major abdominal vessels is demonstrated using artificial models and ultrasound examination on volunteers.
Physiology
The physiology of each system is taught simultaneously with the description of pathological conditions and training in clinical examination methods to identify them. Heart function is taught alongside electrocardiography and its interpretation. The function of the nervous system is taught in conjunction with strokes and the physical examination signs used by the examiner to diagnose them. Bowel function is taught in tandem with palpation and auscultation, which enable the recognition of an ileus, and so on.
Radiology
Every commercial vessel that travels long distances away from ports must be equipped with an X-ray machine. Maritime medics need to have basic knowledge of radiology, starting with a list of kV and mAs values to be used in each case. They should have a fundamental understanding of the images they produce, ensuring that the final result sent to the central station for diagnosis is usable. Additionally, internet connection with the central station is not always guaranteed. As mentioned, radiology is taught alongside anatomy.
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound is a fundamental diagnostic tool of exceptional value. The device that operates it (ultrasound scanner) now fits in the palm of your hand and provides reliable images.
However, the challenge lies in its handling. The operator must correctly direct the beam and move it to produce a series of images that display solid organs and vascular structures.
At HOMED, we place special emphasis on this and teach it alongside anatomy. It is essential for a HOMED-trained maritime medic to be able to image the kidneys, bladder, detect fluid in the chest or abdomen, and assess whether a mass is solid or a fluid-filled cyst.
Electrocardiography (ECG)
At HOMED, we are proud that within just three hours, we can train someone with no prior knowledge of the heart to read an electrocardiogram and describe it reliably to a cardiologist over the phone. For maritime medics, the training is particularly intensive and demanding, enabling the trained seafarer to recognize at least the dangerous arrhythmias immediately, without assistance. Telemedicine systems are not always guaranteed, and addressing certain dangerous arrhythmias requires immediate action.
Physical Examination of the Body
The physical examination of a patient (using hands, eyes, hearing, and smell) often provides a rapid diagnosis, without the need for machines or complex tests.
At HOMED, we train maritime medics to examine patients in such a detailed and reliable way that they often surpass the standard level of medical school graduates. The training is extensive and repetitive, conducted on volunteers who patiently offer their time for this purpose.
Venipuncture
The insertion of a thin tube (venous catheter) into a vein of the body to administer fluids or medications is often life-saving. An example is during hemorrhage. The immediate threat to the patient is not the loss of red blood cells, but rather the sudden decrease in blood volume. Unfortunately, in such cases, the superficial veins become “invisible.” The body hides them to direct blood flow to vital organs. However, this is precisely when venous catheter insertion is crucial and urgent, as the patient’s life depends on it. HOMED has been known for decades throughout Greece and Cyprus for training in DIFFICULT VENIPUNCTURE—specifically, the insertion of a venous catheter in very challenging cases.
Arterial Blood Sampling
Training in arterial blood sampling is essential for analyzing oxygen levels and other critical blood parameters. Participants will practice using specialized models to draw arterial blood and learn how to operate blood gas analyzers. This skill is vital for diagnosing respiratory and metabolic conditions at sea. By becoming proficient in arterial blood sampling, medics can provide accurate information to remote medical professionals, aiding in the management of serious conditions like acidosis or respiratory failure.
Wound Suturing
Wound care is a fundamental aspect of maritime medicine. Participants will receive theoretical instruction in suturing techniques and then apply this knowledge in practical exercises using fresh animal models. These exercises simulate real-life wound types, helping medics develop the necessary skills to close wounds effectively. The ability to suture wounds quickly and accurately is essential for preventing infections and promoting proper healing, particularly in remote maritime environments where immediate hospital access is unavailable.
Tracheal Intubation
In cases of severe respiratory distress, tracheal intubation can be a life-saving procedure. Participants will practice intubation on artificial models, gaining experience with varying levels of difficulty. This training ensures that medics are prepared to manage airways in critical situations, ensuring oxygen delivery when patients cannot breathe adequately on their own. Tracheal intubation is a highly technical skill, and this training offers medics the experience needed to perform it confidently during emergencies.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
CPR is one of the most vital skills for responding to cardiac emergencies at sea. Participants will undergo practical CPR training using mannequins and ventilators, ensuring they can perform life-saving measures when needed. Upon successful completion of the training, participants will receive CPR certification, verifying their ability to perform this critical procedure.
Injections and Blood Draws
Participants will receive training in subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous injection techniques. They will also learn to use a centrifuge for serum separation, which is essential for certain diagnostic tests. Practical exercises will focus on safely administering injections and drawing blood, ensuring participants are capable of performing these tasks efficiently in real-world situations.
Abdominal and Thoracic Paracentesis
Participants will practice paracentesis on specially processed animal cadavers to simulate the removal of fluid from the abdominal or thoracic cavities. This procedure is crucial for diagnosing conditions such as ascites or pleural effusion. Using specialized catheters, medics will learn how to safely perform paracentesis under conditions that closely mimic real-life scenarios.
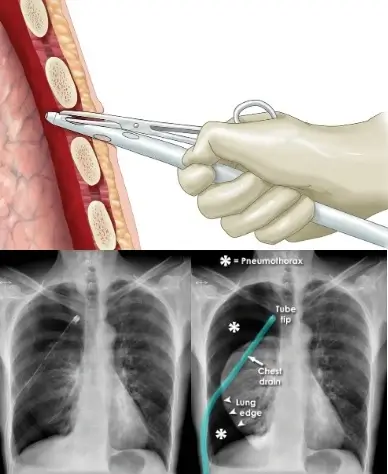
Insertion of Chest Drainage Tube
Chest tube insertion is necessary in cases of pneumothorax or hemothorax, where air or blood accumulates in the chest cavity. Participants will practice inserting Bulaw chest drainage tubes on animal cadavers, gaining experience in handling these life-saving procedures under simulated emergency conditions. This training ensures medics can respond effectively to chest injuries and respiratory crises at sea.
Insertion of Central Venous Catheters
Participants will practice inserting central venous catheters on artificial models and fresh animal models, using both ultrasound guidance and non-ultrasound techniques. This skill is essential for administering medications and fluids in critically ill patients. Training will focus on ensuring precision and safety, even in high-pressure situations.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the duration of the training for Maritime Medics?
-
- The training typically lasts 4-6 weeks, depending on the program. It includes theoretical lessons, hands-on practice, and real-case scenario simulations.
-
-
Is prior medical experience required to participate?
- No, the program is designed for seafarers with no prior medical experience. Full training is provided in both basic and advanced medical skills.
-
What are the benefits of telemedicine for Maritime Medics?
- Telemedicine enables seafarers to have immediate access to doctors onshore. It assists in making accurate decisions and managing emergencies, even in remote areas.