Maritime Medic Support
Managing Femoral Fractures Onboard: The Role of Maritime Medics and Telemedicine Support
Introduction: A Critical Onboard Emergency
Femoral fractures are among the most serious injuries that can occur at sea and require immediate and specialized management. They are usually caused by falls on slippery decks, lifting heavy loads, or blunt trauma during operations onboard. These injuries can lead to severe bleeding, as the femur has a rich blood supply, and significant blood loss often causes shock.
The situation becomes even more challenging due to the limited medical facilities available on ships, making a rapid response crucial. However, with proper training for maritime medics, the use of appropriate medical tools, such as traction splints and intravenous fluids, and the support of telemedicine, maritime medics can respond effectively to such conditions.
This preparation allows for the immediate stabilization of the patient and prevents further complications, such as permanent damage to tissues or nerves. Additionally, effective management reduces the need for costly ship diversions, saving both time and money while ensuring the safety and health of the crew.

Types of Femoral Fractures and Their Implications
Not all femoral fractures are the same. For this reason, understanding their differences is key to determining the best course of action. For example, some fractures require immediate care, while others can be managed onboard until the ship reaches port:
1. Subcapital Fractures (Hip Fractures)
- These fractures are typically less urgent, especially if the bone is not out of place.
- In many cases, the patient can be immobilized and monitored onboard.
- However, delayed treatment may increase the risk of joint damage or loss of blood flow to the bone.
2. Femoral Shaft Fractures (Diaphyseal Fractures)
- These fractures often involve significant bleeding due to the femur’s rich blood supply.
- Without immediate care, they can cause life-threatening complications like hemorrhagic shock.
- Additionally, proper stabilization is needed to avoid further injury to tissues, blood vessels, or nerves.

Challenges of Managing Femoral Shaft Fractures at Sea
Managing femoral shaft fractures onboard is challenging, especially when the vessel is far from medical facilities. Consequently, maritime medics must overcome several obstacles:
1. Severe Bleeding and Shock
Femoral shaft fractures can result in blood loss of up to 1.5 liters. As a result, patients may develop low blood pressure, a rapid heart rate, and pale skin. Therefore, prompt treatment with warmed intravenous fluids is essential to prevent shock and maintain blood circulation.
2. Stabilization
Properly stabilizing the fracture is critical to avoid further complications. For instance, without stabilization, the broken bone may cause additional damage to surrounding blood vessels or tissues. Thus, traction splints are often used to hold the bone in place and reduce bleeding.
3. Remote Medical Settings
Since ships are far from hospitals, access to advanced medical tools is limited. Therefore, maritime medics must rely on their training and guidance from telemedicine doctors to make informed decisions.
The Role of a Trained Maritime Medic
Maritime medics play a key role in treating femoral fractures on ships. Their duties include examining the patient, providing immediate care, and working closely with telemedicine experts:
1. Initial Assessment
- Physical Examination: Medics check for signs like swelling, deformity, or unnatural limb positioning.
- Portable X-rays: When available, imaging confirms the diagnosis and severity of the fracture.

- Shock Identification: Recognizing symptoms like pale skin or weak pulse ensures timely intervention.
2. Stabilizing the Injury
- Using traction splints to stabilize the fracture and reduce bleeding.
- Ensuring minimal movement of the leg to prevent further harm.
3. Replacing Lost Fluids
- Administering warmed intravenous fluids to restore blood volume and prevent shock.
- Monitoring vital signs closely to track the patient’s condition.
4. Managing Pain
- Providing pain relief with NSAIDs or opioids to keep the patient comfortable.
- Relieving pain also helps reduce the patient’s stress and stabilize their overall condition.
5. Collaboration with Telemedicine
Maritime medics must also maintain communication with telemedicine physicians to ensure the best outcomes. For example, they share diagnostic findings such as X-rays and vital signs. Additionally, they follow the doctor’s guidance on whether the patient should stay onboard or be evacuated.
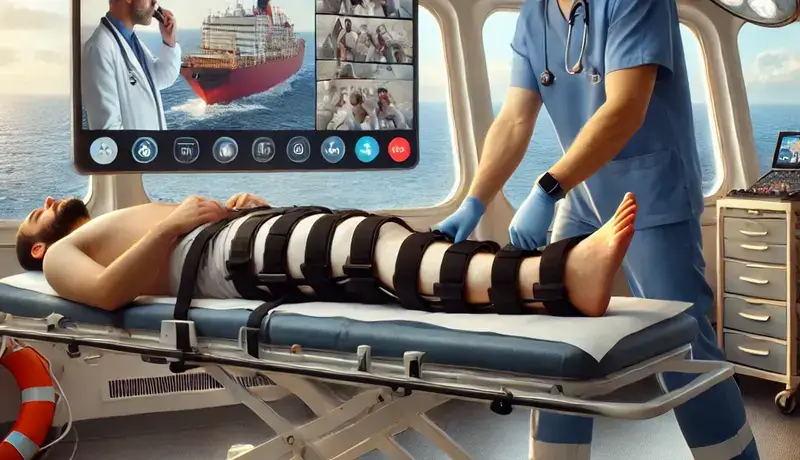
Statistics on Femoral Fractures at Sea
Although femoral fractures are uncommon, they can have severe consequences when they occur. For instance, consider the following statistics:
- Frequency: Femoral fractures account for 2–5% of serious injuries on commercial ships (Oldenburg et al., 2010).
- Ship Deviations: Around 80% of femoral shaft fractures require a ship to divert to a port with hospital facilities.
- Costs:
- Fuel for a 200-mile deviation can cost $30,000–$50,000.
- Delays may cost up to $100,000 depending on the cargo and schedule (Hansen et al., 2017).
Economic Benefits of Preparedness
Investing in training and onboard medical equipment helps reduce both financial and operational impacts. For instance:
- Cost Savings: Avoiding a single ship deviation can save $50,000–$100,000.
- Improved Crew Safety: Proper care leads to faster recovery and greater trust among crew members.
- Enhanced Reputation: Companies that prioritize safety build a positive image and reduce insurance claims.
Conclusion: Why Training and Equipment Are Essential
Femoral fractures are serious injuries that require immediate action, proper training, and advanced tools. A trained maritime medic can:
- Quickly identify and classify the injury.
- Stabilize the patient to prevent further harm.
- Work with telemedicine doctors to decide the best course of action.
By equipping ships with trained medics and the right tools, shipping companies can protect their crew, avoid costly delays, and maintain smooth operations. HOMED’s Maritime Medic Training School and telemedicine services provide the expertise needed to manage such emergencies efficiently.
References
- Oldenburg, M., et al. (2010). “Occupational Accidents on Board Merchant Ships,” Journal of Maritime Health.
- Hansen, H. L., et al. (2017). “Costs of Medical Evacuations and Deviations,” Health Economics Review.
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2020). “Trauma Guidelines for Femoral Fractures.”
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the main causes of femoral fractures at sea?
- Femoral fractures at sea are usually caused by falls on slippery surfaces of the ship, often due to bad weather.
- Other causes include lifting heavy objects without proper technique or protective equipment.
- Additionally, they may result from collisions with objects during daily operations.
2. What can the crew do in case of a fracture if there is no maritime medic onboard?
- The crew can immobilize the injured limb using improvised materials, such as wooden planks or straps, to minimize bone movement.
- It is important to control bleeding by applying pressure to the wound, if present.
- Subsequently, the crew should immediately contact doctors via telemedicine for guidance on the next steps.
3. How do femoral fractures impact the ship’s operations?
- Severe fractures may require the ship to divert to a nearby port, causing delays and financial losses.
- Additionally, an injured crew member reduces the ship’s operational capacity, especially if they held a critical position.
- Finally, the lack of immediate care may worsen the injury, leading to greater health complications for the patient and a drop in crew morale.


